Blog article #4 by Marissa McCarthy (for partial fulfillment of BESC 484 requirement)
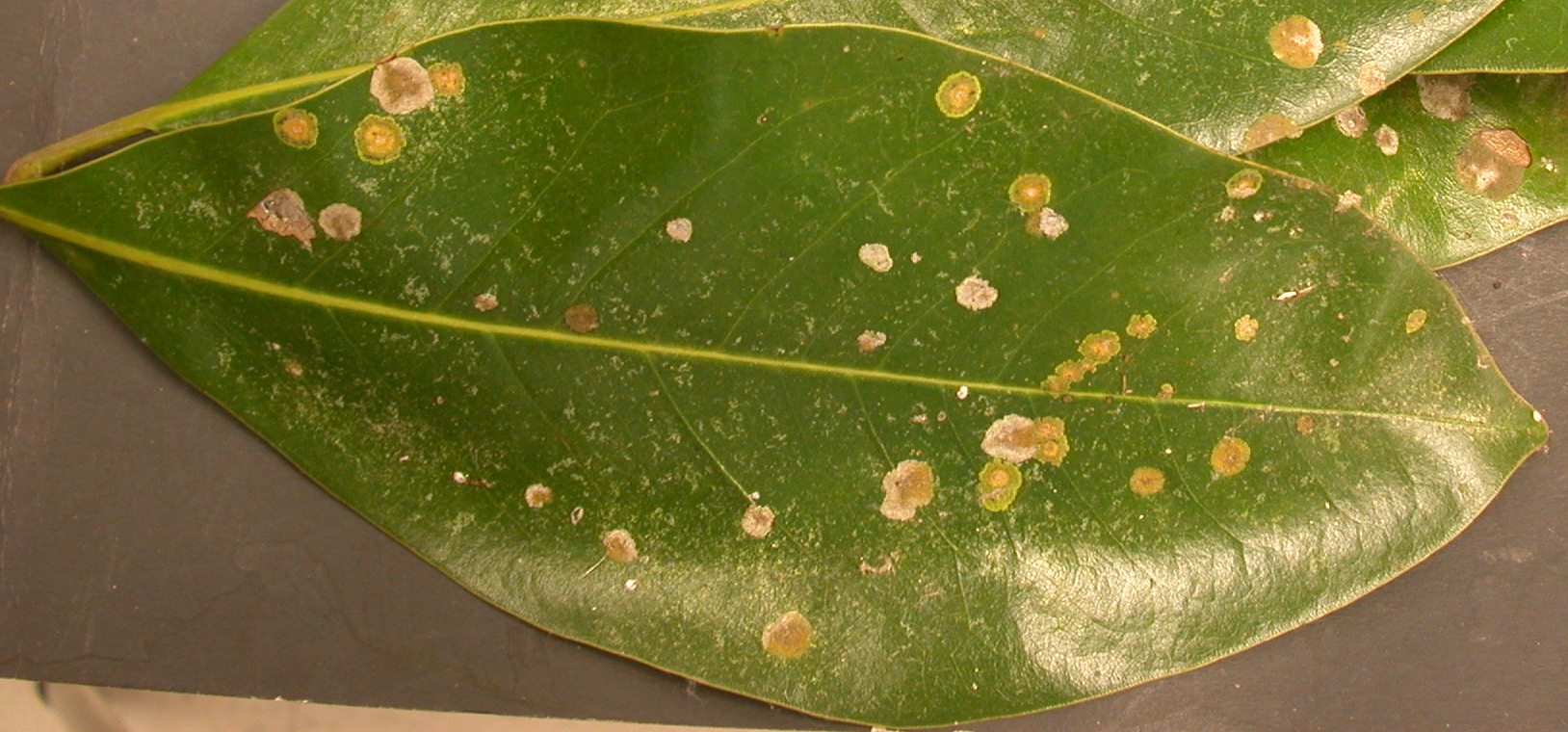
Algal leaf spot is caused by the subcuticular leaf parasite from the genus Cephaleuros. This specific algal leaf spot is C. virescens and was sent into the lab on a magnolia from a private residence. Cephaleuros thrives in environments that are warm with high humidity, or poorly aerated soils. Characteristically this algae is harmless, causing only minor leaf spots on the upper surface of leafs that are raised, textured, orange to brown in color, with filamentous margins. Effects of algal leaf spots on plants are lowered rates of photosynthesis of leaves, defoliation and loss of fruit marketability by damage and spotting, twig dieback and tissue necrosis. Cephaleurosspecies have a discoid thallus and develops in the subcuticular area of the leaves.

Sporangia of the fungus
Reproduction is completed via the production of gametangia and stalked sporangia, which allow motile zoospores to release from the sporangia in the presence of water. Species of Cephaleurosare capable of both asexual and sexual reproduction. The pathogens spores can be disseminated via wind or water splash. Controls used to manage Cephaleuros are accurate diagnosis of the alga, removal of spotted leaves by hand and prune lower branches that are affected, collect and discard all fallen leaves, fungicides (mainly the Bordeaux mixture), spacing between plants and improving soil aeration.
Mentor comment: Be careful of the words used. e.g. 2nd sentence – this algal leaf spot is IDENTIFIED as … AND the pathogen’s spores. Last sentence can be also worded better to discuss the control/management methods. It is also okay to bullet point each of the method. In all – WELL DONE! excellent photos.



